Pain in the metatarsophalangeal joint is a common musculoskeletal condition which is usually observed when abnormal foot biomechanics and long-standing stress deteriorates the anatomical balance of foot.
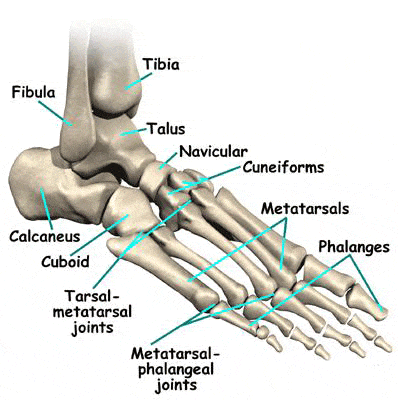
Almost all cases of metatarsal joint pain presents with localized pain, difficulty in walking or just difficulty in maintaining normal day-to-day activities. Patients also report tenderness along the top and bottom surfaces of the foot with limited range of joint motion. Some cases of metatarsophalangeal joint pain are also associated with callus formation underneath the joint surface.
The most common presentation is symptoms are localized warmth, swelling and pain along with on the the bottom and top of the foot (plantar and dorsal aspects.) These symptoms indicate sub-acute or chronic joint inflammation, especially if they are located over a joint.
Certain risk factors can increase the risk of metatarsophalangeal joint pain:
Other less common causes are:
The diagnostic process involve two key elements:
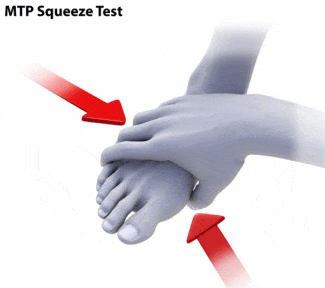
The presence of numbness, burning pain and tingling can indicate a neuralgia / neuroma as opposed to a mechanical cause of metatarsophalangeal joint pain. Likewise the presence of redness, warmth, swelling and edema are suggestive of an active infection.
Treatment mainly revolves around the primary disease process. Injecting local anesthetic solution or corticosteroid can help to reduce inflammation.
Management also involves:
References:


By providing us with your information you are consenting to the collection and use of your information in accordance with our Terms of Service and Privacy Policy.