Reviewed by Janet D. Pearl, MD, MSc
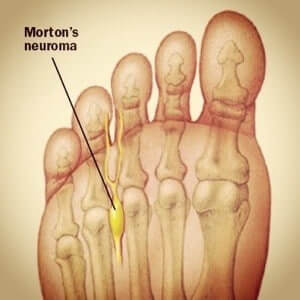
Morton’s neuroma is a complicated and chronic condition of foot in which the patients experience considerable pain and discomfort due to compression of interdigital nerve. In long standing or poorly managed cases, the soft tissues in the surrounding of nerve undergoes fibrotic thickening and swelling. The nerve involvement is reportedly more common in the third web space (between third and fourth toe) due to a variety of anatomical and physiological reasons, but virtually any web-space can be affected.
The pathophysiology of symptoms revolve around persistent and ongoing inflammation and nerve dysfunction due to long standing compression. The symptoms of pain and discomfort typically worsens when a person walks too fast or exert for extended periods of time. Treatment options for Morton’s neuroma include conventional methods, use of drugs and other supportive devices (such as orthotics) in addition to lifestyle and footwear modification.
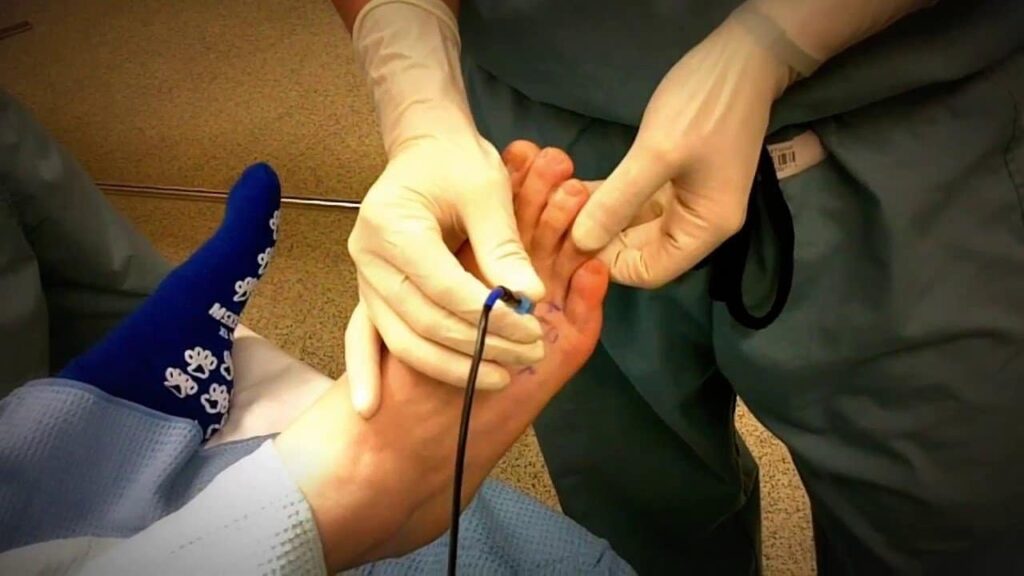
Ultrasound Guided Alcohol Ablation is one of the most preferred modalities of care in the setting of painful neuromas that does not respond to conventional or over-the-counter regimens. The alcohol ablation procedure involves administration of highly concentrated ethanol via injection under ultrasound guidance into the Morton’s neuroma. Despite eh description, the use of local anesthetic makes this procedure irritating but not painful.
The procedure of ethanol ablation involves the insertion of a very thin needle into the Morton’s neuroma under direct ultrasound guidance. To improve the precision, your practitioner will numb the area with the help of local anesthetic agent before administering ethanol injection.
The benefits of using ultrasound guidance are many fold:
Some patients may report localized discomfort that resolves spontaneously within a couple of days and does not require additional treatments.
The average number of therapeutic sessions may range from 1 to rarely 4 (an average of 1-2 sessions to achieve noticeable improvement in symptoms.) According to a recent study(1), close to 80% patients reported satisfactory relief from the painful symptoms at 1-year follow-up.
Ultrasound guided alcohol ablation is an extremely safe and reliable procedure. You can improve the efficacy of procedure by adopting some simple tips:
The risk of major complications or adverse effects is extremely low with procedures like ultrasound guided alcohol ablation. Some post-procedure issues may include:
The success rate of this procedure is usually over 80 %. Very few people may require an additional procedure (such as a repeat alcohol ablation, radiofrequency ablation or rarely even surgical excision of neuroma).
Investigators (2) estimated that the use of ultrasound guidance improves the technical precision of procedure by 100%. It is critical that the clinician performing the procedure be well experienced in doing these procedures under ultrasound guidance. We use nerve stimulator guidance in addition to Ultrasound guidance to further increase the accuracy of the procedure.
References:


By providing us with your information you are consenting to the collection and use of your information in accordance with our Terms of Service and Privacy Policy.