According to a recently published study(1), Morton’s neuroma can be accurately diagnosed by a simple thumb index squeeze test. According to this article this simple test has a 96% sensitivity and a 96% accuracy, making it the most accurate clinical test for Morton’s neuroma.
[The sensitivity is also called the true positive rate, or the recall rate in some fields measures the proportion of actual positives which are correctly identified as such. The accuracy rate is the proportion of true results (both true positives and true negatives) among the total number of cases examined.]
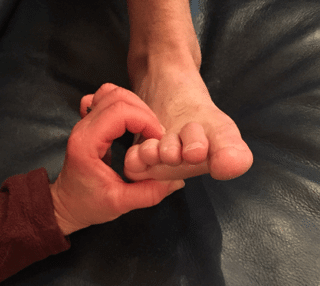
So what is a simple thumb index squeeze test?
Squeeze the symptomatic web space space between the tips of the index finger (on the top of the foot or the dorsal aspect) and thumb (on the bottom of the foot or the dorsal aspect). Splaying of the involved toes was used as a guide for correct positioning and pressure of the thumb and index finger. The test was considered positive if pain was produced.
Remember, Morton’s neuroma is a clinical diagnosis. Your doctor should be well experienced in assessing these patients. Furthermore, MRI and ultrasound both have false negatives and false positives so you can’t fully rely on these tests. If in doubt, a diagnostic local anesthetic injection is the best diagnostic test especially when done under ultrasound guidance by an experienced provider.


By providing us with your information you are consenting to the collection and use of your information in accordance with our Terms of Service and Privacy Policy.