About 30% of the population(1) have asymptomatic Morton’s neuromas. In other words about 1 in 3 people have Morton’s neuroma and so one may consider a Morton’s neuroma a variant of normal. In one study, 54% of the patients had asymptomatic Morton’s neuromas(2).
If you see a Morton’s neuroma on an MRI or ultrasound, it doesn’t help your diagnosis much. Since 1 in 3 people have a Morton’s neuroma, you don’t know if you’re just another one of the 30% of the population who have a non-painful Morton’s neuroma and there is some other condition that is causing your pain or if the Morton’s that you see is the real cause of your pain… Some MRI studies have shown a false positive rate of as high as 40%(3). (A false positive is when you see a Morton’s neuroma on MRI but it is not the cause of your pain.) So a positive radiological diagnosis doesn’t help that much.
Let’s say you don’t see a Morton’s on a MRI or ultrasound examination. Then it also doesn’t help your diagnosis since MRIs (and to a lesser extent ultrasounds) have a well-known level of false negatives for visualization of Morton’s neuromas. So a negative radiological diagnosis doesn’t help that much either.
In other words a positive or negative MRI even ultrasound is not that helpful for the diagnosis of Morton’s neuroma. Some studies have suggested that MRI’s are of little value in the diagnosis of Morton’s neuroma(3).

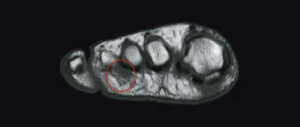
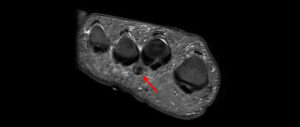
Most importantly, Morton’s neuroma is a clinical diagnosis made by a clinical who is experienced in seeing and treating Morton’s neuroma patients. The diagnosis is made a after a careful assessment of the history and physical examination. In some cases a diagnostic injection may be required. It is not a diagnosis made by any radiological test whether that be an MRI or ultrasound.
Recent studies have shown that ultrasound is a better diagnostic tool than an MRI, although an MRI can be very useful. We only order MRI’s when we have a clinical suspicion that another diagnosis may be present and we want to confirm or exclude that other diagnosis. We also order them in patients who have had Morton’s neuroma surgery or other foot surgery since pain in these patient’s can be quite complicated. There are many diagnoses, which can mimic Morton’s neuroma. See here for a discussion of the diagnoses that can mimic Morton’s neuroma.
In fact, Morton’s neuromas can be so small or even “not present” that after a successful operation to remove the Morton’s neuroma, one may still not know if one had a Morton’s neuroma. Thank about that, if you have the actual nerve section (like you do after a Morton’s neuroma is removed i.e. a neurectomy) you may still not know if you had a Morton’s neuroma because the nerve section may be relatively normal looking even on microscopic and histological examination. Studies have shown that patients with symptoms of Morton’s neuroma can have neuromas which aside from increased demyelination are microscopically and histologically normal when compared to the same nerves in asymptomatic patients(5).
So you can have the nerve removed in an open neurectomy, have the nerve in your hand and have fully recovered and have no further pain – thus a successful operation. Even in this scenario, when you have proven that the neurectomy was successful in treatment, even then the removed nerve section may be virtually normal on microscopic and histological examination. No evidence of a Morton’s neuroma!
The size of your Morton’s neuroma whether measured clinically (after neurectomy removal) or by MRI or by ultrasound is not correlated to the amount of pain that you are suffering(4). So a large Morton’s neuroma may be asymptomatic and not painful while a very small Morton’s neuroma may be extremely painful.


By providing us with your information you are consenting to the collection and use of your information in accordance with our Terms of Service and Privacy Policy.